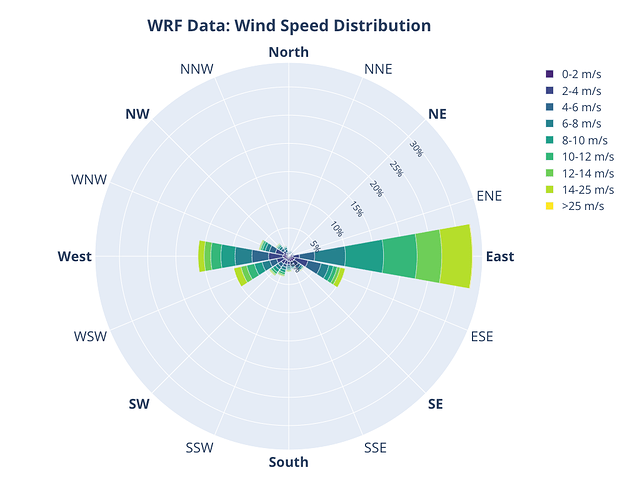
Here is my code, which appeared successful. I am also not a professional programmer, yet this code served me well and provided with a beautiful wind rose. I hope it helps anyone
Data prep:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
#%% function filtering the wind rose data based on the wind speed and direction (NEEDED BELOW)
def wind_dir_speed_freq(boundary_lower_speed, boundary_higher_speed, boundary_lower_direction, boundary_higher_direction):
# mask for wind speed column
log_mask_speed = (wind_rose_data[:,0] >= boundary_lower_speed) & (wind_rose_data[:,0] < boundary_higher_speed)
# mask for wind direction
log_mask_direction = (wind_rose_data[:,1] >= boundary_lower_direction) & (wind_rose_data[:,1] < boundary_higher_direction)
# application of the filter on the wind_rose_data array
return wind_rose_data[log_mask_speed & log_mask_direction]
#%% Wind rose
# Creating a pandas dataframe with 8 wind speed bins for each of the 16 wind directions.
# dataframe structure: direction | strength | frequency (radius)
wind_rose_df = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((16*9, 3)), index = None, columns = ('direction', 'strength', 'frequency'))
directions = ['N', 'NNE', 'NE', 'ENE', 'E', 'ESE', 'SE', 'SSE', 'S', 'SSW', 'SW', 'WSW', 'W', 'WNW', 'NW', 'NNW']
directions_deg = np.array([0, 22.5, 45, 72.5, 90, 112.5, 135, 157.5, 180, 202.5, 225, 247.5, 270, 292.5, 315, 337.5])
speed_bins = ['0-2 m/s', '2-4 m/s', '4-6 m/s', '6-8 m/s', '8-10 m/s', '10-12 m/s', '12-14 m/s', '14-25 m/s', '>25 m/s']
# filling in the dataframe with directions and speed bins
wind_rose_df.direction = directions * 9
wind_rose_df.strength = np.repeat(speed_bins, 16)
#creating a multiindex dataframe with frequencies
idx = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([speed_bins,
directions_deg],
names=['wind_speed_bins', 'wind_direction_bins'])
col = ['frequency']
frequencies_df = pd.DataFrame(0, idx, col)
wind_rose_data = meteo[['wind_speed_m/s', 'wind_direction_deg']].to_numpy()
# distance between the centre of the bin and its edge
step = 11.25
# converting data between 348.75 and 360 to negative
for i in range(len(wind_rose_data)):
if directions_deg[-1] + step <= wind_rose_data[i,1] and wind_rose_data[i,1] < 360:
wind_rose_data[i,1] = wind_rose_data[i,1] - 360
# determining the direction bins
bin_edges_dir = directions_deg - step
bin_edges_dir = np.append(bin_edges_dir, [directions_deg[-1]+step])
# determining speed bins ( the last bin is 50 as above those speeds the outliers were removed for the measurements)
threshold_outlier_rm = 50
bin_edges_speed = np.array([0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 25, threshold_outlier_rm])
frequencies = np.array([])
# loop selecting given bins and calculating frequencies
for i in range(len(bin_edges_speed)-1):
for j in range(len(bin_edges_dir)-1)
bin_contents = wind_dir_speed_freq(bin_edges_speed[i], bin_edges_speed[i+1], bin_edges_dir[j], bin_edges_dir[j+1])
# applying the filtering function for every bin and checking the number of measurements
bin_size = len(bin_contents)
frequency = bin_size/len(wind_rose_data)
#obtaining the final frequencies of bin
frequencies = np.append(frequencies, frequency)
# updating the frequencies dataframe
frequencies_df.frequency = frequencies*100 # [%]
wind_rose_df.frequency = frequencies*100 # [%]
# calling the PLOT function
"""
PLOTTING THE ROSES
"""
fig_wind_rose = wind_rose_fig(frequencies_df,
title = '<b>WRF Data: Wind Speed Distribution</b>',
filename= 'fig_wind_rose_WRF.png',
open_bool = False)
The plotting function goes here:
import plotly.graph_objects as go
from plotly.offline import plot
def wind_rose_fig(frequencies_df, title, filename, open_bool):
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('0-2 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='0-2 m/s',
marker_color='#482878'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('2-4 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='2-4 m/s',
marker_color='#3e4989'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('4-6 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='4-6 m/s',
marker_color='#31688e'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('6-8 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='6-8 m/s',
marker_color='#26828e'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('8-10 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='8-10 m/s',
marker_color='#1f9e89'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('10-12 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='10-12 m/s',
marker_color='#35b779'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('12-14 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='12-14 m/s',
marker_color='#6ece58'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('14-25 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='14-25 m/s',
marker_color='#b5de2b'))
fig.add_trace(go.Barpolar(
r=frequencies_df.loc[('>25 m/s'), 'frequency'],
name='>25 m/s',
marker_color='#fde725'))
fig.update_traces(text=['North', 'NNE', 'NE', 'ENE', 'East', 'ESE', 'SE', 'SSE', 'South', 'SSW', 'SW', 'WSW', 'West', 'WNW', 'NW', 'NNW'])
fig.update_layout(
title=title,
title_font_size=26,
title_x = 0.463,
legend_font_size=18,
polar_radialaxis_ticksuffix='%',
polar_angularaxis_rotation=90,
polar_angularaxis_direction='clockwise',
polar_angularaxis_tickmode = 'array',
polar_angularaxis_tickvals=[0, 22.5, 45, 72.5, 90, 112.5, 135, 157.5, 180, 202.5, 225, 247.5, 270, 292.5, 315, 337.5],
polar_angularaxis_ticktext=['<b>North</b>', 'NNE', '<b>NE</b>', 'ENE', '<b>East</b>', 'ESE', '<b>SE</b>', 'SSE', '<b>South</b>', 'SSW', '<b>SW</b>', 'WSW', '<b>West</b>', 'WNW', '<b>NW</b>', 'NNW'],
polar_angularaxis_tickfont_size = 22,
polar_radialaxis_tickmode = 'linear',
polar_radialaxis_angle = 45,
polar_radialaxis_tick0 = 5,
polar_radialaxis_dtick = 5,
polar_radialaxis_tickangle = 100,
polar_radialaxis_tickfont_size = 14)
fig.write_image(get_fig_dir() + filename, width = 1000, height = 800)
fig.show(renderer = 'png', width = 1000, height = 800)
return plot(fig, auto_open = open_bool)
#%% histogram with wind directions
def histogram_wind_dir_fig(data, name, color, title, xaxis_title, yaxis_title, filename, open_bool):
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(go.Histogram(
x=data,
histnorm='percent',
name=name, # name used in legend and hover labels
xbins=dict( # bins used for histogram
size=3),
marker_color=color))
fig.update_layout(
title_text = title, # title of plot
title_x=0.5,
title_font_size = 24,
xaxis=dict(title = xaxis_title,
titlefont_size=20,
tickfont_size=16,
tickvals=[0,30,60,90,120,150,180,210,240,270,300,330,360],
ticktext=['N',30,60,'E',120,150,'S',210,240,'W',300,330,'N']), # xaxis label
yaxis=dict(title = yaxis_title,
titlefont_size=20,
tickfont_size=16), # yaxis label
bargap=0.2,) # gap between bars of adjacent location coordinates
fig.write_image(get_fig_dir() + filename, width = 1200, height = 500)
fig.show(renderer = 'png', width = 1200, height = 500)
return plot(fig, auto_open = open_bool)