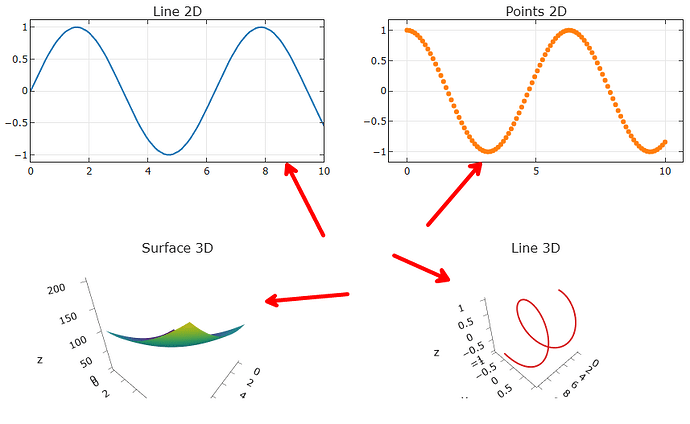
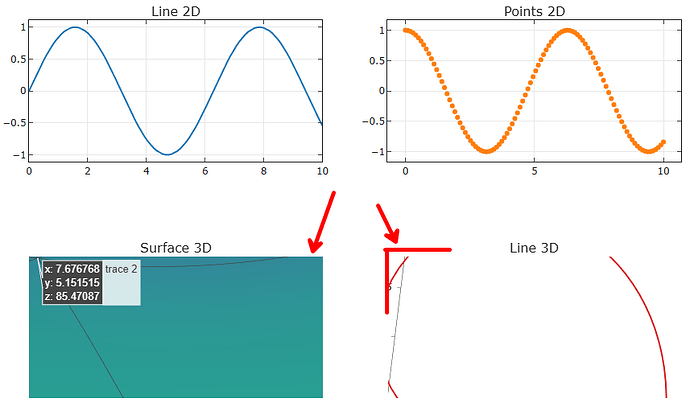
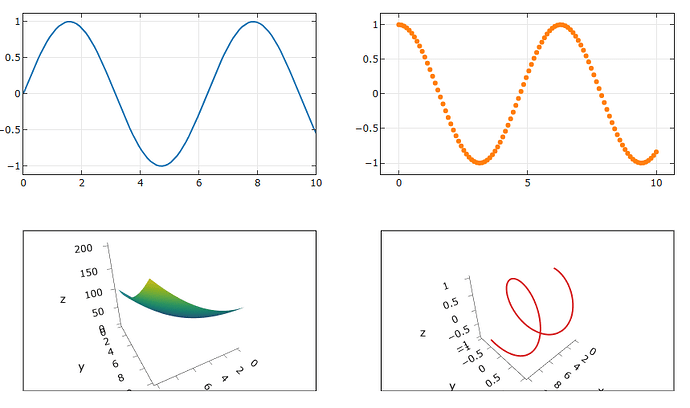
Thanks! I think that adjusting the coordinates solved the problem, because I really need to work with one figure, not in jupyter environment. So, I had to add 2 shapes.
I also had some struggle with the template="simple_white" setting, needing to set manually fillcolor, layerand opacity, but I think it worked in the end.
I final code became:
import numpy as np
import plotly.graph_objects as go
from plotly.subplots import make_subplots
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
z = np.cos(x)
sh_x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
sh_y = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
sh_x, sh_y = np.meshgrid(sh_x, sh_y)
sh_z = sh_x**2 + sh_y**2
fig = make_subplots(
rows=2,
cols=2,
specs=[
[{"type": "xy"}, {"type": "xy"}],
[{"type": "scene"}, {"type": "scene"}],
],
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode="lines"),
row=1,
col=1,
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Scatter(x=x, y=z, mode="markers"),
row=1,
col=2,
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Surface(z=sh_z, x=sh_x[0], y=sh_y[:, 0], colorscale="Viridis", showscale=False),
row=2,
col=1,
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Scatter3d(x=x, y=y, z=z, mode="lines", line=dict(width=4)),
row=2,
col=2,
)
fig.update_layout(
height=800,
width=900,
showlegend=False,
)
fig.add_shape(
type="rect",
xref="paper",
yref="paper",
x0=0,
y0=0,
x1=0.45,
y1=0.425,
line=dict(color="black", width=1),
layer="below",
fillcolor="white",
opacity=1.0,
)
fig.update_layout(
template="simple_white",
plot_bgcolor="white",
height=500,
margin=dict(l=50, r=40, t=30, b=0),
)
fig.update_xaxes(mirror="allticks", ticks="inside", showgrid=True)
fig.update_yaxes(mirror="allticks", ticks="inside", showgrid=True)
fig.add_shape(
type="rect",
xref="paper",
yref="paper",
x0=0.55,
y0=0,
x1=1,
y1=0.425,
line=dict(color="black", width=1),
layer="below",
fillcolor="white",
opacity=1.0,
)
fig.show()
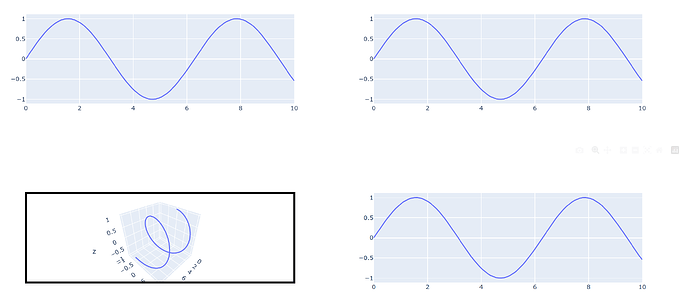
With result: