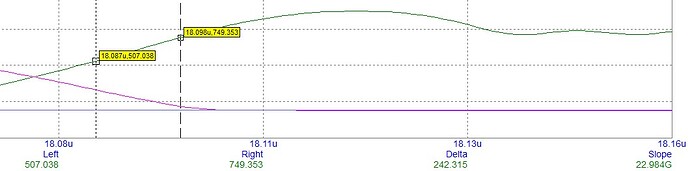
Hi,
I’m searching for a solution to implement the functionality to add two cursors to the plot and measure the difference using python plotly. Like in an digital oscilloscope. Can anybody help me with how this could be achieved?. If not python plotly, is there any other way i can achieve this using a different library in python ?
3 Likes
+1
I would also need something like that. Would be great to add as much as we want!
1 Like
Hi,
I also want to develop a functionality with two cursors to measure the difference as oscilloscope. Does anybody found a solution?
Hi @Stunkata
Welcome to the community ![]()
Old post, but how about using Dash? Something like:
Code
from dash import dcc, Input, Output, callback, Dash, State, Patch
import plotly.graph_objects as go
app = Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dcc.Graph(id='cool-graph', figure=go.Figure(layout_dragmode='drawline'))
@callback(
Output('cool-graph', 'figure'),
Input('cool-graph', 'relayoutData'),
State('cool-graph', 'figure')
)
def update_graph(_, fig):
shape_patch = Patch()
if 'shapes' in fig['layout'].keys():
for i, shape in enumerate(fig['layout']['shapes']):
if shape['type'] == 'line':
delta_x, delta_y = shape['x1'] - shape['x0'], shape['y1'] - shape['y0']
d = (delta_x ** 2 + delta_y ** 2) ** 0.5
shape_patch['layout']['shapes'][i]['label'][
'text'] = f'd: {d:.2f} (∆x: {delta_x:.2f}, ∆y: {delta_y:.2f})'
return shape_patch
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run_server(debug=True)

You can add as many lines as you want clicking on the figure and drag the existing ones to update the values
Hi,
thank you for the answer. But no, it is not possible to use Dash…i have an Vue3 app and i need to integrate functionallity as a digital oscilloscope in there.
Oh ! Too bad, I can’t help with Vue… ![]()